20+ Years Of Experience as Fertility Specialists
20 Years Of Experience as a Fertility Specialists
National Fertility Awards 2023
Call Us
+919990044555
In vitro fertilization (IVF) has revolutionized the field of reproductive medicine, offering hope to millions of couples struggling with infertility. One crucial aspect of the IVF process is blastocyst implantation, a complex and intricate event that determines the success of the treatment.
This article delves into the IVF blastocyst implantation process, shedding light on its mechanisms, the factors that can influence its outcome, and the potential benefits and risks associated with this procedure.
By gaining a deeper understanding of blastocyst implantation, patients can make more informed decisions when it comes to fertility treatments and enhance the chances of achieving a successful pregnancy.
If You Want to Know More Details – Find Out Which Month is the Perfect Time for IVF in India
- What is blastocyst implantation?
Blastocyst implantation is a critical stage in the early development of an embryo during which it attaches itself to the uterine lining, also known as the endometrium. This process is essential for the establishment of a successful pregnancy.
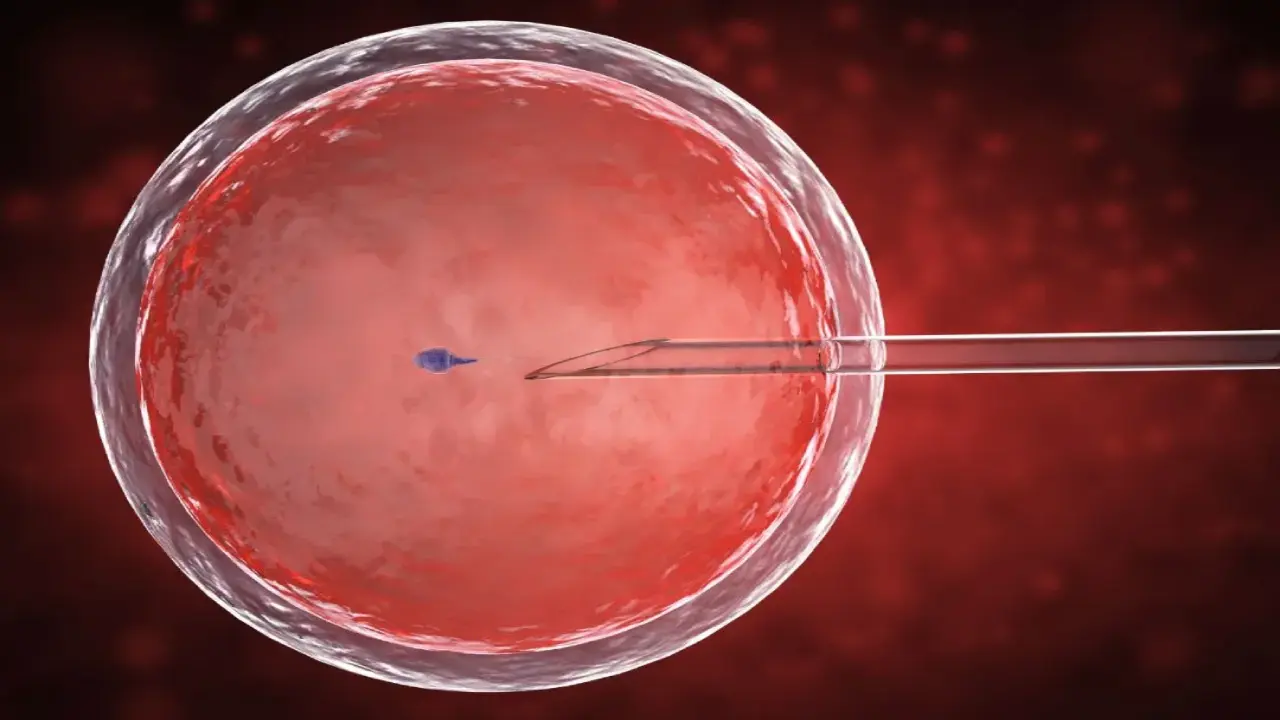
In the context of in vitro fertilization (IVF), blastocyst implantation refers to the point at which a fertilized egg, which has been cultured in a laboratory for around 5-6 days and developed into a blastocyst, is transferred into the woman’s uterus with the aim of achieving a successful pregnancy.
The blastocyst is a more advanced stage of embryonic development, consisting of a fluid-filled cavity and two distinct cell types: the inner cell mass, which eventually forms the fetus, and the outer layer of cells called the trophectoderm, which develops into the placenta.
Book An Appointment
Follow Us On
How does Blastocyst Implantation Occur?
Blastocyst implantation is a complex and highly orchestrated process involving several crucial steps:
- Hormonal changes: As the menstrual cycle progresses, hormonal changes prepare the endometrium for implantation. The hormone estrogen promotes endometrial thickening, while progesterone helps to create a receptive environment.
- Blastocyst development: After fertilization, the embryo undergoes multiple cell divisions over 5-6 days, transforming from a morula into a blastocyst. The blastocyst features an inner cell mass (future fetus), an outer layer called the trophectoderm (future placenta), and a fluid-filled cavity.
- Blastocyst hatching: The blastocyst must “hatch” from its protective outer shell, known as the zona pellucida, in order to implant successfully. Enzymes secreted by the trophectoderm help break down this shell, allowing the blastocyst to emerge.
- Endometrial receptivity: For successful implantation, the endometrium must be receptive to the blastocyst. This receptive phase, called the “window of implantation,” typically occurs around 6-10 days after ovulation. Various proteins and molecules are involved in creating a receptive endometrium, facilitating communication between the blastocyst and the uterine lining.
- Apposition and adhesion: The trophectoderm cells of the hatched blastocyst make initial contact with the endometrial surface, a process known as apposition. Next, the blastocyst firmly adheres to the endometrium through cellular interactions and molecular signaling.
- Invasion and embedding: The trophectoderm cells begin to invade the endometrial tissue, secreting enzymes that break down the extracellular matrix and allow the blastocyst to burrow into the uterine lining. This process, known as embedding, facilitates the formation of the placenta and establishes a connection between the developing embryo and the maternal blood supply.
- Decidualization: The endometrial cells surrounding the implanted blastocyst undergo a transformation called decidualization, which supports the ongoing growth and development of the embryo.
- Through these intricate steps, blastocyst implantation establishes the foundation for a successful pregnancy.
How is Blastocyst Implantation Performed in IVF?
In IVF, blastocyst implantation is performed through a process called embryo transfer. Here’s an overview of the steps involved in this procedure:
- Blastocyst culture: After fertilization, the embryos are cultured in the laboratory for 5-6 days until they reach the blastocyst stage, which consists of an inner cell mass, a fluid-filled cavity, and an outer layer of cells called the trophectoderm.
- Blastocyst selection: The embryologist evaluates the blastocysts based on their morphology, growth rate, and overall quality. The healthiest and most viable blastocyst(s) are chosen for transfer to increase the chances of successful implantation.
- Preparation for transfer: The woman’s uterine lining is prepared for implantation using hormonal medications (estrogen and progesterone) to ensure optimal receptivity during the embryo transfer.
- Embryo transfer procedure: On the day of the transfer, the selected blastocyst(s) is carefully loaded into a thin, flexible catheter. The physician then gently guides the catheter through the cervix and into the uterus, where the blastocyst(s) is released. This procedure is typically painless and does not require anesthesia.
- Progesterone support: Following the transfer, the woman continues to take progesterone supplements to help maintain a receptive endometrium and support the early stages of pregnancy.
- Pregnancy test: Approximately 9-14 days after the embryo transfer, a blood test is performed to check for the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced by the developing placenta. A positive test indicates that the blastocyst has implanted successfully and a pregnancy has been established.
By carefully performing the blastocyst implantation in IVF through embryo transfer, fertility specialists aim to maximize the chances of achieving a successful pregnancy while minimizing potential risks.
What are the Factors that Can affect Blastocyst Implantation?
Several factors can influence the success of blastocyst implantation, including:
- Embryo quality: The overall health and genetic makeup of the blastocyst play a significant role in implantation success. Embryos with chromosomal abnormalities or developmental defects may fail to implant or result in early pregnancy loss.
- Endometrial receptivity: The readiness of the uterine lining to accept the blastocyst is crucial for successful implantation. Hormonal imbalances, infections, or structural abnormalities can negatively impact endometrial receptivity.
- Synchronization: The timing of blastocyst development and endometrial receptivity must be synchronized to ensure successful implantation. Disruptions to this delicate balance can lead to implantation failure.
- Maternal age: As a woman’s age increases, the likelihood of successful implantation decreases, primarily due to a decline in egg quality and an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
- Lifestyle factors: Poor nutrition, obesity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and high stress levels can all negatively impact blastocyst implantation and overall fertility.
- Uterine abnormalities: Structural issues within the uterus, such as fibroids, polyps, or congenital malformations, can interfere with blastocyst implantation.
- Immune system factors: Certain autoimmune conditions or immunological factors can lead to implantation failure by affecting the communication between the blastocyst and the endometrium or causing inflammation in the uterine lining.
- Medical conditions: Conditions like endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or thyroid disorders can impact hormonal balance and affect blastocyst implantation.
- IVF-related factors: The quality of the IVF laboratory, culture media, and the skill of the embryologist can all influence the development and viability of the blastocyst, ultimately affecting implantation success.
Understanding and addressing these factors can help improve the chances of successful blastocyst implantation and increase the likelihood of a healthy pregnancy.
How long does a blastocyst take to implant after IVF?
After an embryo transfer in IVF, a blastocyst typically takes around 1-2 days to implant into the uterine lining. The process of implantation begins shortly after the transfer, and the blastocyst starts to attach itself to the endometrium within 24 hours. Complete implantation, which involves the blastocyst fully embedding itself into the uterine lining and establishing connections with the maternal blood supply, usually occurs by day 5 or 6 after the transfer.
It’s important to note that the timing of implantation can vary slightly between individuals. Following implantation, it takes another few days for the developing placenta to produce enough human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to be detected in a blood test. As a result, pregnancy tests are generally performed about 9-14 days after the embryo transfer to confirm if a successful implantation and pregnancy have occurred.
How successful is IVF with blastocyst transfer?
IVF success rates with blastocyst transfer tend to be higher compared to the transfer of embryos at earlier stages, such as the cleavage stage (2-3 days after fertilization). The main reasons for this increased success rate are:
- Improved embryo selection: By culturing embryos to the blastocyst stage, embryologists can better evaluate their quality, growth rate, and overall viability, which helps in selecting the healthiest embryo(s) for transfer.
- Greater developmental potential: Blastocysts have a higher developmental potential than cleavage-stage embryos, as they have already undergone several cell divisions and are closer to the stage where implantation occurs naturally.
- Better synchronization: Transferring blastocysts allows for better synchronization between the embryo and the endometrial receptivity, increasing the chances of successful implantation.
- Reduced risk of multiple pregnancies: With blastocyst transfer, fewer embryos are typically transferred, reducing the risk of multiple pregnancies. This is because transferring one or two high-quality blastocysts has a better chance of resulting in a successful pregnancy compared to transferring multiple cleavage-stage embryos.
However, it’s important to note that IVF success rates are influenced by various factors, such as maternal age, fertility issues, embryo quality, and the expertise of the fertility clinic. Generally, younger women have higher success rates, with the chances of success decreasing as maternal age increases.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the average live birth rate per transfer for women under 35 years old using fresh embryos from non-donor eggs is around 46.8% for blastocyst transfer. This percentage decreases with age, dropping to approximately 16.6% for women aged 41-42 and further declining for older age groups.
Keep in mind that individual success rates may vary, and it’s essential to discuss your specific situation and chances of success with your fertility specialist.
Advice for couples undergoing IVF treatment
Undergoing IVF treatment can be an emotional and challenging journey for couples. Here are some pieces of advice to help you navigate the process and maintain a healthy mindset:
- Do your research: Educate yourselves about the IVF process, success rates, and potential risks. This knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions and have realistic expectations throughout the treatment.
- Choose the right fertility clinic: Select a clinic with a good reputation, experienced staff, and high success rates. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and seek recommendations from others who have undergone IVF.
- Communicate openly: Maintain open communication with your partner, sharing your feelings, concerns, and expectations. Support each other emotionally and remember that you’re in this journey together.
- Stay organized: Keep track of appointments, medications, and important information related to your treatment. Staying organized can help reduce stress and ensure a smoother experience.
- Prioritize self-care: Take care of your physical and emotional well-being by eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, and practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation or yoga.
- Seek professional support: If needed, consult with a mental health professional, such as a therapist or counselor, to help cope with the emotional challenges associated with IVF.
- Build a support network: Connect with friends, family members, or support groups who can offer understanding, encouragement, and advice throughout your IVF journey.
- Be patient: Remember that IVF may not always result in success on the first attempt. It’s essential to remain patient and be prepared for the possibility of multiple cycles or alternative plans.
- Focus on the bigger picture: Keep in mind that the ultimate goal is to create a loving family. Stay focused on this objective and try not to get lost in the details and challenges of the IVF process.
- Acknowledge your emotions: It’s normal to experience a wide range of emotions during IVF treatment, from hope and excitement to frustration and disappointment. Allow yourself to feel these emotions and give yourself grace as you navigate this complex journey.
By following this advice, couples undergoing IVF treatment can better cope with the challenges they may face and improve their overall experience. Stay positive, support each other, and remember that every couple’s journey is unique.
if you want to know more details: 11 Tips To Choose A Fertility Specialist In Delhi?
Wrapping up
blastocyst implantation plays a crucial role in the success of in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatments. Understanding the intricate process of blastocyst implantation and the factors that can affect its outcome is essential for patients seeking fertility treatments. By gaining insight into the mechanisms of blastocyst implantation, patients can make informed decisions and increase their chances of achieving a successful pregnancy.
Blastocyst implantation involves the attachment of a developed blastocyst to the uterine lining, signaling the establishment of a successful pregnancy. Hormonal changes, blastocyst development, hatching, endometrial receptivity, apposition, adhesion, invasion, and embedding are all crucial steps in the process.
Share this with
Related Videos
What is TORCH test in infertility and why is it done?
There are numerous tests that are available to infertile couples that are recommended by some doctors, which might help them determine the cause of their infertility. One such test is the TORCH test.
What is Prolactin Hormone?
Prolactin is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland present at the brain’s base. It is best known for its role in lactation, or milk production, in breastfeeding women.However, Prolactin also plays other important roles in both men and women, such as regulating the immune system, stimulating the growth of new blood vessels, and influencing behaviour and reproductive function. In this blog, we will explore what Prolactin is, how it works, and what happens when there are imbalances in prolactin levels.
Follow Us On
About Author